Fauna of the Kara Sea
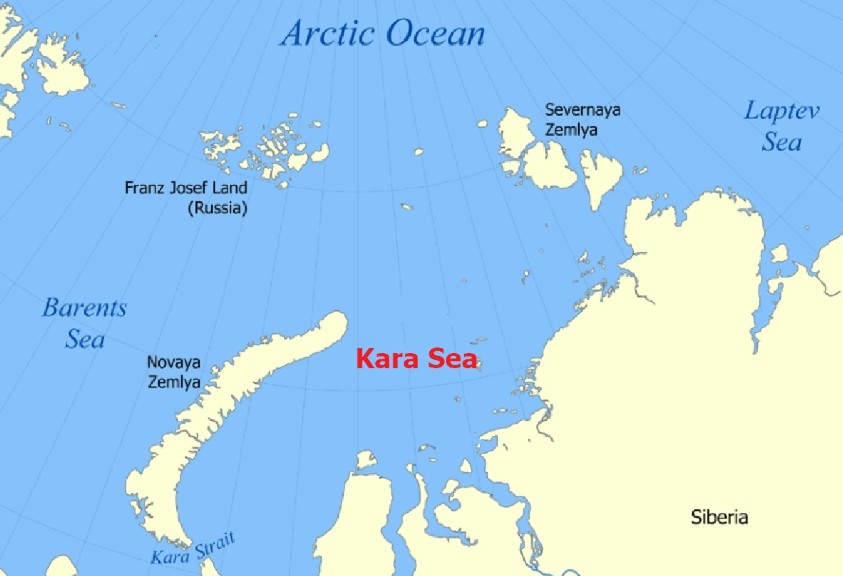 A marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bordered by the northern coast of Eurasia and several islands: Vaygach, Novaya Zemlya, Franz Josef Land, Severnaya Zemlya and Heiberg. Wiese Island is located in the northern part of the sea. It is mainly located on the shelf and has many islands. The full-flowing rivers Ob and Yenisei empty into the sea, causing significant variation in salinity. The Taz and Pur rivers also flow into the sea.
A marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bordered by the northern coast of Eurasia and several islands: Vaygach, Novaya Zemlya, Franz Josef Land, Severnaya Zemlya and Heiberg. Wiese Island is located in the northern part of the sea. It is mainly located on the shelf and has many islands. The full-flowing rivers Ob and Yenisei empty into the sea, causing significant variation in salinity. The Taz and Pur rivers also flow into the sea.
The Kara Sea is dominated by depths ranging from 50 to 100 meters, with a maximum depth of 620 meters. It covers an area of 893,400 km². It is one of the coldest seas. Until modern climate warming occurred, a large part of the sea was covered by perennial ice, and the water temperature only rose above 0°C in summer near the mouths of rivers. Fog and storms are frequent. The sea is covered with ice for most of the year.
In winter, the water temperature near the sea surface is close to the freezing point of -1.8 °C. In shallow areas, the water is well mixed from the surface to the bottom, and it has the same temperature and salinity (approximately 34 parts per million). Warmer water from the Barents Sea penetrates the troughs. At depths of 150 to 200 meters, there is a layer of water with a temperature of up to 2.5 °C and a salinity of 35 ppm. In summer, river runoff and ice melting lead to a decrease in seawater salinity below 34 ppm. In estuaries, the water becomes nearly fresh. In the upper 50-70 meters (only 10-15 meters in the east), the water warms up to +6°C in summer (only +2°C in the north).
Flora and fauna of the Kara Sea
The sea's flora and fauna are shaped by heterogeneous climatic and hydrological conditions in the north and south. Neighboring basins also influence the area due to the migration of warm-loving species from the Barents Sea and highly arctic species from the Laptev Sea. The ecological boundary of their distribution is approximately the eightieth meridian. Freshwater elements also play a significant role in the sea's ecosystem.
The flora and fauna of the Kara Sea are poorer than those of the Barents Sea but richer than those of the Laptev Sea. The Kara Sea has 114 fish species, the Barents Sea has 54, and the Laptev Sea has 37. The invertebrate fauna is quite diverse. The sea's zooplankton consists mainly of copepods, krill, chaetognaths, pteropods, and jellyfish, which serve as food for a few cetacean species. The flora is represented by bottom algae.
Fish in the Kara Sea
The following species are of fishery importance in the Kara Sea: European plaice (Pleuronectes platessa), European smelt (Osmerus eperlanus), saffron cod (Eleginus gracilis), pollock (Pollachius virens) from the Gadidae family, and Arctic cisco (Coregonus autumnalis), muksun (Coregonus muksun), and vendace (Coregonus albula) from the Coregonus. Salmonidae include nelma (Stenodus nelma), Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha), chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta), pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha), and sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Coregonus and salmon spawn in rivers and migrate to the open sea to fatten up. They stay near the mouths of rivers and do not move far north. Small fish, such as capelin (Mallotus villosus), common seasnail (Liparis liparis), and Arctic alligatorfish (Aspidophoroides olrikii), thrive here. Since most of the Kara Sea is covered with ice, fishing mainly occurs in river mouths, bays, coves, and the coastal zone.
Mammals of the Kara Sea
Pinnipeds found in this marine area include ringed seals (Pusa hispida), bearded seals (Erignathus barbatus), and walruses (Odobenus rosmarus). Cetacean species present include fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus), sei whales (Balaenoptera borealis), blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus), common minke whales (Balaenoptera acutorostrata), and humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae). Beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) enter the area in large numbers during the summer months. Bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) and orcas (Orcinus orca) occasionally migrate here from the Barents Sea. As in all northern coastal seas, walruses are harvested here, but only to meet the needs of the local population, as they are protected.
Kara Sea sharks
The only confirmed species of shark in this sea is the Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus), the northernmost and cold-loving shark species. During the winter, they can be found in the surf zone, in shallow bays, and near the surface of river mouths. In the summer, they stay at depths ranging from 180 to 550 meters. They are not of interest to local residents because they are a commercial species with low numbers and low-quality meat. A basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) from the Barents Sea is theoretically possible, but they have not yet been seen here. Spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) are unlikely to be seen in the coastal zone away from freshwater river estuaries. None of these shark species are dangerous to humans.
Saffron cod
Latin nameEleginus gracilisOther namesWachna cod, Pacific navaga.IdentificationThe lower jaw is shor..
Salmon, Chinook
Latin name Oncorhynchus tshawytscha Other names King salmon, spring salmon, tyee, quinnat, tule, ..
Salmon, Chum
Latin name Oncorhynchus keta Other names Calico salmon, dog salmon, fall salmon, autumn salmon, c..
Salmon, Pink
Latin name Oncorhynchus gorbuscha Other names Humpback salmon, humpy, fall salmon, pink, humpback..
Salmon, Sockeye
Latin name Oncorhynchus nerka Other names Sockeye, red salmon, blueback salmon, big redfish; Fren..
Salmonidae
Salmonidae is a family of fishes of the order Salmoniformes. Passable and freshwater fishes. They li..
Shark, Basking
Latin name Cetorhinus maximus Other names No information Identification The dark gray or slate-..
Smelt
Latin name Osmerus eperlanus Other names European Smelt Identification Like salmon and trout, t..
Vendace
Vendace are two species of fish in the genus whitefish, family Whitefish.European (Coregonus albula)..









