Fauna of the Greenland Sea
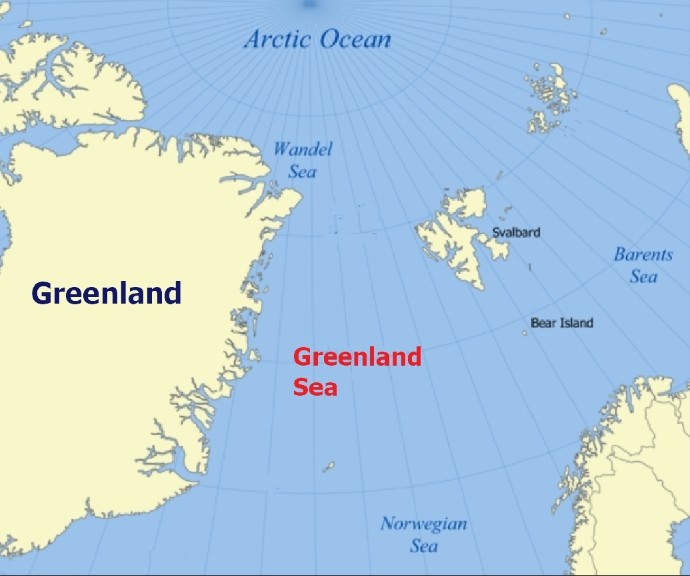 The Greenland Sea is a marginal part of the Arctic Ocean, located between the islands of Greenland, Iceland, Svalbard, Spitsbergen, Medway and Jan Mayen. The total area of the sea is about 1205000 km², the average depth is 1444 meters, the deepest depth is 5527 meters. The climate is arctic and varies considerably over the vast sea area. Temperatures range from -49°C along the Greenland coast in winter to 25°C south of Svalbard in summer. The average temperature in February, the coldest month, is -10°C in the south and -26°C in the north. The corresponding values for the warmest month, August, are 5 °C in the south and 0 °C in the north. Summers are very short: the number of days per year with temperatures above 0 °C varies from 225 in the north to 334 in the south. Annual rainfall is 250 mm in the north and 500 mm in the south. Northerly winds persist throughout the year, cooling surface waters and bringing ice to the south. Average surface water temperatures are about -1°C or less in the north and 1-2°C in the south. Corresponding summer temperatures are about 0 and 6 °C. Water temperatures in the south are below -1°C. The salinity of the surface water is 3.30-3.45% in the eastern part and below 3.20% in the western part, increasing to 3.49% towards the bottom. The water is green. The tides are semidiurnal with an average height of 4.4 meters. Together with the currents, they break up the floating ice sheets and mix the different layers of water both laterally and in depth. All of the colder water from the North Atlantic Current that enters the Greenland Sea sinks into the Arctic Ocean before returning south as the colder surface East Greenland Current, which is an important part of the Atlantic Conveyor Belt and runs along the western part of the sea. Along the eastern part is the warm Svalbard Current, part of the Gulf Stream. The mixing of cold, desalinated water from the ice melt with the warm, salty Svalbard Current can result in a mixing of waters that promotes thermohaline circulation. The combination of these processes creates a counterclockwise current in the central part. Because of the frequent fog, winds and currents that constantly transport ice and icebergs southward, the sea has a narrow window for commercial shipping around the Greenland coast - the ice season begins in October and ends in August. There are three types of floating ice in the sea: Arctic pack ice up to a few meters thick, sea ice about a meter thick, and freshwater icebergs. The eastern part of the sea up to the northern tip of Spitsbergen does not freeze in winter. Since the latitude of this point is usually above 80 degrees, this part of the sea is the highest latitude tip of the world's oceans that is free of ice throughout the year.
The Greenland Sea is a marginal part of the Arctic Ocean, located between the islands of Greenland, Iceland, Svalbard, Spitsbergen, Medway and Jan Mayen. The total area of the sea is about 1205000 km², the average depth is 1444 meters, the deepest depth is 5527 meters. The climate is arctic and varies considerably over the vast sea area. Temperatures range from -49°C along the Greenland coast in winter to 25°C south of Svalbard in summer. The average temperature in February, the coldest month, is -10°C in the south and -26°C in the north. The corresponding values for the warmest month, August, are 5 °C in the south and 0 °C in the north. Summers are very short: the number of days per year with temperatures above 0 °C varies from 225 in the north to 334 in the south. Annual rainfall is 250 mm in the north and 500 mm in the south. Northerly winds persist throughout the year, cooling surface waters and bringing ice to the south. Average surface water temperatures are about -1°C or less in the north and 1-2°C in the south. Corresponding summer temperatures are about 0 and 6 °C. Water temperatures in the south are below -1°C. The salinity of the surface water is 3.30-3.45% in the eastern part and below 3.20% in the western part, increasing to 3.49% towards the bottom. The water is green. The tides are semidiurnal with an average height of 4.4 meters. Together with the currents, they break up the floating ice sheets and mix the different layers of water both laterally and in depth. All of the colder water from the North Atlantic Current that enters the Greenland Sea sinks into the Arctic Ocean before returning south as the colder surface East Greenland Current, which is an important part of the Atlantic Conveyor Belt and runs along the western part of the sea. Along the eastern part is the warm Svalbard Current, part of the Gulf Stream. The mixing of cold, desalinated water from the ice melt with the warm, salty Svalbard Current can result in a mixing of waters that promotes thermohaline circulation. The combination of these processes creates a counterclockwise current in the central part. Because of the frequent fog, winds and currents that constantly transport ice and icebergs southward, the sea has a narrow window for commercial shipping around the Greenland coast - the ice season begins in October and ends in August. There are three types of floating ice in the sea: Arctic pack ice up to a few meters thick, sea ice about a meter thick, and freshwater icebergs. The eastern part of the sea up to the northern tip of Spitsbergen does not freeze in winter. Since the latitude of this point is usually above 80 degrees, this part of the sea is the highest latitude tip of the world's oceans that is free of ice throughout the year.
Common Inhabitants of the Greenland Sea
The marine flora is represented by phytovorgae typical of Arctic waters, mainly diatoms, although some coastal species are also found. The waters are rich in plankton and benthos, vital for many inhabitants. The coastal areas of the islands are inhabited by coelenterates, molluscs, crustaceans and other benthic life. These small invertebrates and small organisms are eaten by larger invertebrates, fish (such as cod, herring, redfish, halibut and plaice) and mammals (including various species of seals, whales and dolphins). Scallops, northern prawns, snow crabs and sea urchins (caviar) are harvested for export to other countries. Unfortunately, the marine flora and fauna are in a vulnerable state due to the effects of climate change, pollution and expanding industrial activities.
Greenland Sea Fish World
The fish world of this sea is quite rich. Its cold waters are home to commercial species such as Polar cod (Boreogadus saida), Arctic cod (Arctogadus glacialis), Navaga (Eleginus nawaga), Beaked redfish (Sebastes mentella), Arctic flounder (Liopsetta glacialis), Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides), Haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus), Capelin (Mallotus villosus), Pollock (Pollachius virens), Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus), Greenland cod (Gadus ogac), Northern wolffish (Anarhichas denticulatus), Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus), Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Unfortunately, the flora and fauna of the sea have become vulnerable due to the effects of climate change, pollution and expanding industrial activities.
Sharks in the Greenland Sea
Only the Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) feels comfortable in the waters of this sea. It easily tolerates the harsh climate due to the high content of fatty tissue in its body. Less common are the Porbeagle (Lamna nasus), and Spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias). They also do well in many northern seas. Theoretically, it is quite possible to live in the sea and the oldest representative of sharks - Basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus), which prefers cool waters with moderate climate and in search of food can overcome great distances, including the open ocean. But even large species of all these fearsome fish are only potentially dangerous to humans.
Mammals of the Greenland Sea
The Greenland Sea is home to many species of rorquals, dolphins and killer whales. The local bowhead whale has a tragic history of survival. For centuries, whalers have hunted these amazing mammals, greatly reducing their numbers. Although it is now illegal to hunt them, their population has barely recovered. Pinnipeds are represented by several species of seals (Hooded seal, Bearded seal, Common seal) as well as small herds of walruses. Fur seals, Harp seals, Ringed seals and walruses are fished in these waters today. Fishing for Beluga whales, Fin whales, Narwhals, Sei whales and porpoises is limited.
Arctic cod
Latin nameArctogadus glacialisOther namePolar codIdentificationArctic cod are characterized by a thi..
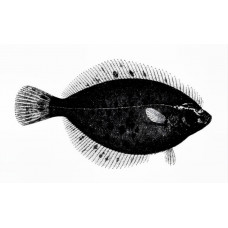
Arctic flounder
Latin nameLiopsetta glacialisOther nameChristmas flounder, eelback flounder and Polar plaice.Identif..
Beaked redfish
Latin nameSebastes mentellaOther namesDeepwater redfin, ocean perch, Atlantic redfish, Norway haddoc..
Benthos
From the Greek bénthos - depth.The aggregate of organisms living on and in the substrate of marine a..
Boreogadus saida
Boreogadus saida is a marine fish of the cod family. The eyes are large. There is a very short anten..
Capelin
Latin name Mallotus villosus Other names Danish/Dutch/German/ Norwegian: lodde; French: capelin a..
Charr, Arctic
Latin name Salvelinus alpinus Other names Seagoing fish: char, red charr; Cree: awanans; Da..
Crustaceans
Crustacea is a class of invertebrates of the Arthropoda type. It includes animals with body length f..
Dogfish, Spiny
Latin name Squalus acanthias Other names Dogfish, dog shark, grayfish, Pacific grayfish, Pacific ..
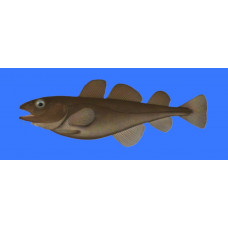
Greenland cod
Latin nameGadus ogacOther nameGadus callarias marisalbi, Gadus maris-albi Iljin, Gadus morhua marisa..
Greenland halibut
Latin nameReinhardtius hippoglossoidesOther namesGreenland turbotIdentificationThe body is elongated..
Greenland Shark
Latin nameSomniosus microcephalusOther namesGurry shark, grey shark, Somniosus microcephalusIdentifi..
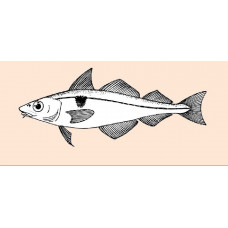
Haddock
Latin name Melanogrammus aeglefinus Other names Haddie, scrod; French: eglefin; Italian: asinello..
Halibut, Atlantic
Latin name Hippoglossus hippoglossus Other names Common halibut, giant halibut, right-eyed flound..
Herring
Latin name Clupea Other names American Shad, Atlantic Herring, Alewife, Threadfin Shad Identific..