Latin name
Liopsetta glacialis
Other name
Christmas flounder, eelback flounder and Polar plaice.
Identification
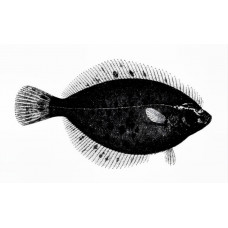
It is a right eyed flounder. It is characterized by the presence of both eyes on the same side of the head, normal scales and generally uniform coloration. Lateral line with a very low curve over the pectoral fin, straight posteriorly and with a short appendage on the head; 73-76 pores on the main part; in males it is complete, but in females measuring about 20 cm there is an open groove on the posterior part of the body. Vertebrae: 37-38.
Features of fish fins
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Dorsal soft rays (total): 50 - 62; Anal spines: 1; Anal soft rays: 35 - 44. The most anterior dorsal ray of these fishes is located above the eye; anal ray with anterior spearhead in front of the first ray; caudal ray rounded.
Fish colouring
The upper side of the body of the Arctic flounder is dark olive green to dark brown, sometimes with black spots; the underside is white. Fins are pale brown, sometimes with a yellow tinge or faint dark spots.
Distribution
The Arctic flounder's natural habitat is the polar waters of the northeastern Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, from the White and Barents Seas to the coasts of Siberia in Russia and Queen Maud Bay in Canada, and from the Chukchi and Bering Seas to Bristol Bay in Alaska and the northern part of the Sea of Okhotsk.
Habitat
It is a bottom-dwelling fish that lives on muddy coastal bottoms in saline, brackish, and freshwater at depths down to 300 feet (90 meters).
Size
The maximum length of males of this species is 44.0 cm and the total length is 25.0 cm. The reported maximum age is 26 years.
Behavior
Coastal species, not found far from the shore. It inhabits shallow waters and temporarily enters rivers, freshets, estuaries and lakes. In the evening, especially at high tide, it comes closer to the shore. Apparently they go out to sea in the fall and to shore in the spring.
Food and feeding habits
The diet of these fish consists mainly of small fish and zoobenthos invertebrates such as amphipods, mollusks and marine worms.
Reproduction
The reproductive cycle of these fish is thought to occur only once every two years. They breed in the winter under ice at subzero water temperatures. Their eggs are floating (pelagic). Their development takes about two to three months. The larvae hatch in spring, during the period of abundant development of plankton necessary for their nutrition.
Fishing
The species is of minor commercial interest.
Relationship with a person
Harmless.
| Classification | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Squad | Carangiformes |
| Family | Pleuronectidae |
| Genus | Liopsetta |
| Species | L. glacialis |
| Features | |
| Conservation status | Least Concern |
| Habitat | Bottom |
| Life span, years | 26 |
| Maximum body weight, kg | No information |
| Maximum length, cm | 44 |
| Sailing speed, m/s | No information |
| Threat to people | Edible |
| Way of eating | Predator |
Arctic flounder
Tags: arctic flounder