Latin name
Limanda aspera
Other names
Limanda asprella Hubbs, Pleuronectes asper Pallas.
Identification
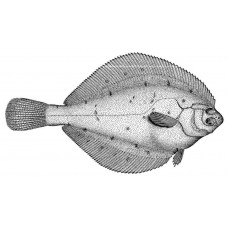
Body large and broad, mouth small. The lateral line is strongly curved above the pectoral fins. The snout is very short, its length not exceeding the diameter of the eye. The lateral line has 80-89 scales.
Fish colouring
A narrow black stripe runs along the dorsal and anal fins on the eye side. Blind side white, dorsal and anal fins yellow from underneath with bluish-grey margin and white ray tips.
Distribution
Widespread, inhabiting the seas of the North Pacific, penetrating along the Asian coast to Busan, along the American coast to Vancouver Island, entering the Chukchi Sea in the north.
Habitat
Leads a benthic lifestyle. It stays close to the shore at a depth of 15-80 metres, mainly over sandy substrates. In winter it moves away from the coast to deeper depths, staying mainly at 250-400 metres.
Size
A large flounder that can reach a length of 49 cm and a weight of 1.7 kg.
Behavior
It winters at depths of 150-250m, but in April, after the longhead, it comes to the coast to spawn, where it remains until September.
Food and feeding habits
Their diet is based on crustaceans, molluscs, worms and small fish.
Reproduction
Spawning takes place near the coast in shallow water. It usually peaks in mid-summer. Fecundity is relatively high.
Fishing
It is a valuable commercial species with an excellent flavour.
| Classification | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Squad | Pleuronectiformes |
| Family | Pleuronectidae |
| Genus | Limanda |
| Species | L. aspera |
| Features | |
| Conservation status | Least Concern |
| Habitat | Bottom |
| Life span, years | 13 |
| Maximum body weight, kg | 1,7 |
| Maximum length, cm | 49 |
| Sailing speed, m/s | No information |
| Threat to people | Edible |
| Way of eating | Predator |
Yellowfin sole
Tags: yellowfin sole