Latin name
Micromesistius australis
Other names
Micromesistius australis Norman (1937), Southern blue whiting, southern poutassou (English), merlan bleu austral, poutassou (French), polaca (Spanish), polaca (Portuguese).
Identification
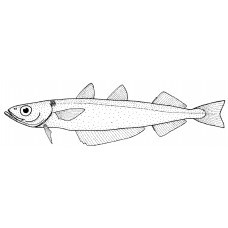
The body is elongated and covered with lightly falling cycloid scales. The length of the snout is almost equal to the diameter of the eye. The lower jaw is longer than the upper and projects slightly forward. The tendril on the lower jaw is absent. The three dorsal fins are separated by large gaps. Two anal fins; the first has a long base from the beginning of the first dorsal fin to the beginning of the base of the third dorsal fin. There are no hard, unbranched rays on the dorsal and anal fins. A distinctive features of the species is the number of gill stamens on the first gill ray (38-48), which is considerably more than in northern whiting. The lateral line runs along the entire body and over the head. The colour of the back is dark, the sides are blue or blueish, the belly is almost white.
Distribution
It is widespread in the temperate and subantarctic waters of the southern hemisphere. Two subspecies are distinguished: Micromesistius australis australis Inada et Nakamura, 1975 occurs from 38 to 62° S in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean around the Falkland Islands and along the coast of Argentina, as well as in the waters around the South Orkney Islands, the South Shetland Islands, the South Georgia Archipelago and the Skosha Sea. It is recorded in the southeastern Pacific off the coast of Chile. The second subspecies, Micromesistius australis pallidus Inada et Nakamura, 1975, occurs in the southwestern Pacific Ocean around the South Island of New Zealand. Several isolated populations exist.
Habitat
Schooling pelagic and demersal fish. It lives at depths of 70 to 800 metres above the continental shelf during the summer months and above the continental slope during the winter months. The New Zealand subspecies prefers slightly greater depths.
Size
Maximum body length is 90 cm, usually 40-50 cm. Maximum body weight is 1350 g. Life expectancy is 23 years.
Life history and Behavior
It makes seasonal migrations, moving south to the Antarctic coast in the summer.
Food and feeding habits
Juveniles and adults feed on plankton, mainly amphipods, euphausiids and copepods. Less commonly, the diet includes cephalopods and small fish such as luminescent anchovies.
Reproduction
They reach sexual maturity at the age of 3-5 years with a body length of 30-40 cm. Spawning occurs off the coast of New Zealand in June-September and off the coast of Argentina in spring (September-October). Eggs are pelagic and hatch at depths of 150-400 metres. Fecundity ranges from 20 to 130 thousand eggs.
| Classification | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Squad | Gadiformes |
| Family | Gadidae |
| Genus | Micromesistius |
| Species | M. australis |
| Features | |
| Habitat | Pelagic |
| Life span, years | 23 |
| Maximum body weight, kg | 0,9 |
| Maximum length, cm | 90 |
| Threat to people | Edible |
| Way of eating | Predator |
Southern blue whiting
Tags: southern blue whiting