Latin name
Liparis tunicatus
Other name
Liparis arctica, liparis herschelinus, liparis steineni, liparis tunicatus.
Identification
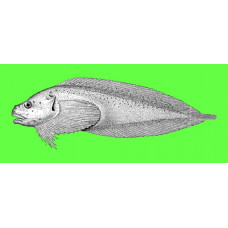
The Kelp Snailfish has a broad, rounded head that is slightly compressed from the sides. It has a somewhat blunted snout. The space between the eyes is flat and slightly depressed; the occiput is somewhat convex. The upper jaw is slightly longer than the lower jaw. The 3-lobed teeth are arranged in approximately 30 oblique rows. The eyes are small with a diameter 6.3 times the length of the head and 2.7 times the distance between the eyes. The length of the snout is 2.4 times the length of the head, and the length of the upper jaw is twice that. The head is 4 times the length of the body. The gill slits are equal in length to the distance between the eyes. Their lower end is at the level of the ninth ray of the pectoral fin. This feature likely changes with age. The posterior nostrils end in short, compressed tubes located in front of the eyes at a distance equal to half the diameter of the eye. The anterior nostrils are simple and located immediately in front of the posterior nostrils at a distance equal to half the diameter of the eye.
The body is broad and high in the front, gradually thinning and lowering towards the rear. At the beginning of the dorsal fin, the body is 5.3 times its absolute length; at the base of the caudal fin, it is about 0.5 times the diameter of the eye. The entire torso is covered in sagging skin. On the upper side of the torso and the top of the head, there are sparse but numerous bony spicules that protrude from the skin. These spines probably do not develop in young fish. There is a small gill opening. The kelp snailfish is sometimes confused with the juveniles of the related species L. gibbus.
Features of fish fins
The dorsal fin begins at the level of the posterior end of the skin lobe of the gill cover. Its first 12 rays are short and hidden in the skin. Then, they gradually lengthen, reaching their maximum length at the end of the second third of the fin. At this point, their length is three-quarters of the body's height and equal to 2.33 times the diameter of the eye. The anal fin is the same height as the dorsal fin. The upper end of the pectoral fin reaches the level of the beginning of the anal fin. The length of the 11th ray is 1.2 times the length of the head. The rays of the lower pectoral fin blade extend halfway between the posterior margin of the sucker and the anal opening. The length of the pelvic sucker is 1.5 times its width, which is 7.2 times the length of the body excluding the head.
Fish colouring
The Kelp Snailfish has a grayish body with dark brown and reddish spots on its dorsal side, which are especially numerous on its caudal part. The head is the same color. The fins are gray with no evident banding. There may be light stripes.
Distribution
This species of fish inhabits the Arctic and northwestern Atlantic oceans. It is found at least in the vicinity of Greenland and Franz Josef Land.
Habitat
This species of fish can be found in offshore and near-bottom waters at depths ranging from 0 to 620 meters (0 to 2,034 feet).
Size
The maximum total length of this fish is approximately 6.5 inches (16.5 cm).
Behavior
The kelp snailfish is one of the northernmost species in its family, alongside species such as Liparis bathyarcticus and L. fabricii. It lives among algae.
Food and feeding habits
This species of fish feeds on small crustaceans that live on the ocean floor.
Reproduction
In March, they spawn in Franz Josef Land at depths of 6-25 meters (20-82 feet), laying eggs in bunches that attach to algae.
Fishing
This species is not commercially important.
Relationship with a person
This is a type of fish that is harmless to humans.
| Classification | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Squad | Perciformes |
| Family | Liparidae |
| Genus | Liparis |
| Species | L. tunicatus |
| Features | |
| Conservation status | Not Evaluated |
| Habitat | Bottom |
| Life span, years | No information |
| Maximum body weight, kg | No information |
| Maximum length, cm | 16,5 |
| Sailing speed, m/s | No information |
| Threat to people | Not edible |
| Way of eating | Bentophage |
Kelp snailfish
Tags: kelp snailfish