Latin name
Selar crumenophthalmus
Other name
Big-eyed scad, purse-eyed scad, goggle-eyed scad, akule, chicharro, charrito ojón, jacks, matang baka, mushimas and coulirou.
Identification
The species name is derived from the Greek ὀφθαλμός 'eye' and Latin crumena 'leather purse or wallet', and is related to the fatty eyelid that almost completely covers the eye; the remaining vertical slit resembles the opening of a purse.
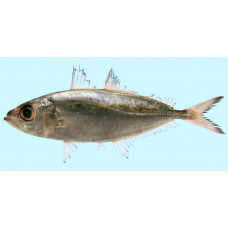
The body is elongated, slightly compressed at the sides. Fine cycloid scales cover the entire body, except for a small patch of bare skin behind the pelvic fins. The lower profile of the body is slightly more convex than the upper.
The eyes are very large, their diameter slightly less than the length of the snout; they are almost completely covered by the fatty eyelid, only a small vertical slit in the centre of the eye remains open. The tip of the maxilla is broad, extending to a vertical line passing through the anterior margin of the eye.
There are 9-12 gill stamens on the upper part of the first gill arch and 27-31 gill stamens on the lower part.
The lateral line forms a low, elongated arch anteriorly and then continues straight to the caudal peduncle. The length of the chorda of the curved part of the lateral line is almost equal to the length of the straight part. The curved part has 48-56 scales and 0-4 bony flaps; the straight part has 0-11 scales and 29-42 bony flaps. Scutellum relatively small.
The teeth on both jaws are small and curved. On the lower jaw, the teeth are arranged in an irregular row. On the upper jaw, the teeth are arranged in a narrow band that narrows at the sides.
Vertebrae: 10 dorsal and 14 caudal vertebrae.
Features of fish fins
Edge of secondary pectoral girdle (cleithrum) with deep furrow with large tubercle below and small tubercle at upper edge of furrow. Two dorsal fins. The first dorsal fin has 8 hard rays and the second has 1 hard ray and 24-27 soft rays. The anal fin has 1 barbed ray and 21-23 soft rays, with 2 barbs in front of the fin. The last soft ray of the dorsal and anal fins is not separated from the other rays. Pectoral fins short (shorter than the length of the head), sickle-shaped. Caudal fin sickle-shaped.
Fish colouring
Upper third of body and top of head blue with metallic tinge or bluish green. Lower third of body and head silvery or whitish. A broad band of yellow colour runs from the posterior edge of the gill cover to the top of the caudal peduncle. A small black oval spot near the edge of the gill cover. First dorsal fin translucent with dark edges; second dorsal fin dark with blackish anterior part; anal fin translucent or slightly dark at base; caudal fin dark with dark tip of upper lobe; pectoral fins translucent or slightly dark at base, sometimes with yellowish tinge; pelvic fins translucent.
Distribution
Widespread in tropical and warm temperate waters of all oceans. Western Atlantic: from Nova Scotia along the US coast to Bermuda and the Bahamas; Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean; along the coast of South America to Rio de Janeiro. Eastern Atlantic: from Senegal to southern Angola, including Cape Verde, Ascension and St Helena islands. Indo-Pacific: from the east coast of Africa along South and Southeast Asia to Japan and Australia. Pacific Ocean: the Hawaiian Islands. Eastern Pacific: from Baja California and the Gulf of California to Ecuador and around oceanic islands such as the Galapagos Islands.
Habitat
Marine pelagic fish. Found in clear, transparent waters around oceanic islands and in coastal waters at depths of 1 to 170 m; occasionally found in turbid waters.
Size
The maximum length of this species is 70 cm. Maximum recorded age: 3 years.
Behavior
During the day, these fish form aggregations of several hundred to several thousand individuals. At night they disperse in search of food.
Food and feeding habits
Feeds on benthic and pelagic invertebrates, zooplankton and small fish.
Reproduction
The female of this fish lays a large number of eggs. Absolute fecundity can be as high as 200,000 eggs. The larvae and juveniles that hatch from the eggs often swim under the domes of sea jellyfish to protect themselves from predators. Juveniles feed on zooplankton.
Fishing
Commercial fish. The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand and Venezuela are the biggest fishers. Fishing is by trawl, longline, purse seine and cast seine. It is sold fresh, salted and dried.
Relationship with a person
Reports of ciguatera poisoning.
| Classification | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Squad | Carangiformes |
| Family | Carangidae |
| Genus | Selar |
| Species | S. crumenophthalmus |
| Features | |
| Conservation status | Least Concern |
| Habitat | Pelagic |
| Life span, years | 3 |
| Maximum body weight, kg | No information |
| Maximum length, cm | 70 |
| Sailing speed, m/s | No information |
| Threat to people | Edible |
| Way of eating | Predator |
Bigeye scad
Tags: bigeye scad