Latin name
Hippoglossoides robustus
Other names
Hippoglossoides robustus
Identification
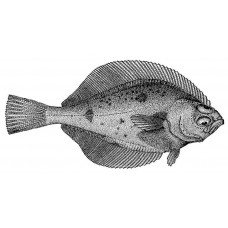
The mouth is large. The teeth on each jaw are arranged in a single row. The front teeth on each jaw are slightly enlarged, not resembling canines. The upper eye is completely lateral. The upper surfaces of the eyeballs are not scaly. The interorbital space is narrow, not ribbed and covered with several rows of scales. The lateral line is curved above the pectoral fins.
Features of fish fins
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Dorsal soft rays (total): 67-80; Anal spines: 0; Anal soft rays: 51-62. Caudal fin slightly rounded.
Fish colouring
The ocular side is light brown with small dark spots, which may be on the blind side of the body; in juveniles it is lighter, brownish-yellow, with numerous small brownish spots, and there are also rare larger dark spots on the bases of the dorsal and anal fins and on the midbody. The blind side of the body is milky grey. The peritoneum is black, giving the outside of the abdomen a blackish tinge.
Distribution
Its natural habitat is the North Pacific Ocean, from Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk through the Blazing Sea to Alaska, the Aleutian Islands and the Arctic coast of Canada.
Habitat
A marine, oceanodromous, bottom-dwelling species found at depths of up to 425 metres (1,394 feet).
Size
Reaches 30 centimetres in length.
Behavior
In winter, the main concentrations are distributed at depths of 90-120 m at the edge of the continental shelf, where the lower zone of waters formed as a result of winter cooling is located. The aggregations and the fish that form them are sedentary. In summer, the aggregations move to shallower depths of 30-90 m and disperse over a larger area.
Food and feeding habits
Molluscs and crustaceans form the basis of the diet. Euphausiaceae are common, Crangonidae, Gammaridae, Amphipoda, Sipuncula and Priapulida are less common. Six fish species were found in the diet.
Reproduction
Feeding and spawning take place in the same areas of the shelf at depths of 26-100 metres. Spawning lasts 3.5 months and occurs from April to August, depending on the area. Eggs are small, 1.6-2.1 mm in diameter, pelagic. Larvae hatch at about 4 mm. Metamorphosis begins at 10 mm in length and ends with the transition to a benthic lifestyle at 27-31 mm in length.
Fishing
The fishery value is unknown as flatfish are not counted by species in the catches of commercial vessels.
Relationship with a person
Its meat is light and tender. It is recommended for regular consumption by people with iodine deficiency.
| Classification | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Squad | Pleuronectiformes |
| Family | Pleuronectidae |
| Genus | Hippoglossoides |
| Species | H. robustus |
| Features | |
| Conservation status | Least Concern |
| Habitat | Bottom |
| Life span, years | No information |
| Maximum body weight, kg | No information |
| Maximum length, cm | 30 |
| Sailing speed, m/s | No information |
| Threat to people | Edible |
| Way of eating | Predator |
Bering flounder
Tags: bering flounder