Latin name
Trachurus indicus
Other name
Trachurus indicus
Identification
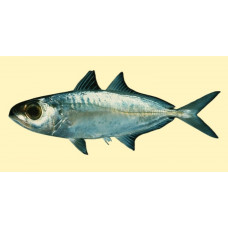
The Arabian Scad has an elongated and slightly compressed body, with approximately equal upper and lower profiles. The eye is moderately large and has a well-developed fatty eyelid which usually covers almost the entire eye, except for a vertical oval with the pupil in the centre. The upper jaw is fairly broad and extends to the front of the eye. The mouth is equipped with small teeth, one row in each jaw. The scales on the lateral line are large and form shields.
Features of fish fins
The fish has two separate dorsal fins, the first with 8 hard rays and the second with one hard ray and 28-35 soft rays. The anal fin has 2 separate spines at the front followed by a hard ray and 24-30 soft rays. The length of the pectoral fins is equal to or greater than the length of the head.
Fish colouring
Arabian scads have a black spot on the upper edge of the gill cover, and the upper body is dark to almost black or greenish to bluish, while the sides and belly are silvery to white. The fins are colourless.
Distribution
Widespread in the western Indian Ocean from the Red Sea and Somalia through the Persian Gulf east to Pakistan and south to the Saya de Malha Bank. The species was first recorded in the Mediterranean off Turkey in 2004.
Habitat
It is a semi-pelagic, benthic fish that inhabits depths from 20 to 250 metres, but is most commonly recorded at depths of less than 100 metres. It does not appear to be recorded where water temperatures are below 20°C or where oxygen saturation is less than 30%.
Size
The maximum total length is 35 centimetres. Males of this species reach a total length of 20 centimetres.
Behavior
Arabian scad form schools in coastal waters.
Food and feeding habits
The diet of the Arabian scad consists mainly of fry and small crustaceans.
Reproduction
Sexual maturity occurs in the first year of life when the fish reaches a length of 11 centimetres. However, in the waters off Oman, sexual maturity occurs at a total length of about 16.3 centimetres for males and 17.4 centimetres for females. Spawning occurs in the Gulf of Oman from August to November, peaking in September and October. They reach an age of at least seven years and the estimated generation length is three and a half years.
Fishing
This fish is caught as by-catch in some fisheries and is often discarded due to its low market value. It and two related species are targeted by purse seine fisheries in the Gulf of Suez, while it is caught for subsistence in Somalia.
Relationship with a person
Harmless.
| Classification | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Squad | Carangiformes |
| Family | Carangidae |
| Genus | Trachurus |
| Species | T. indicus |
| Features | |
| Conservation status | Vulnerable |
| Habitat | Pelagic |
| Life span, years | 3,5 |
| Maximum body weight, kg | No information |
| Maximum length, cm | 35 |
| Sailing speed, m/s | No information |
| Threat to people | Edible |
| Way of eating | Predator |
Arabian scad
Tags: arabian scad