Fauna of the Somov Sea
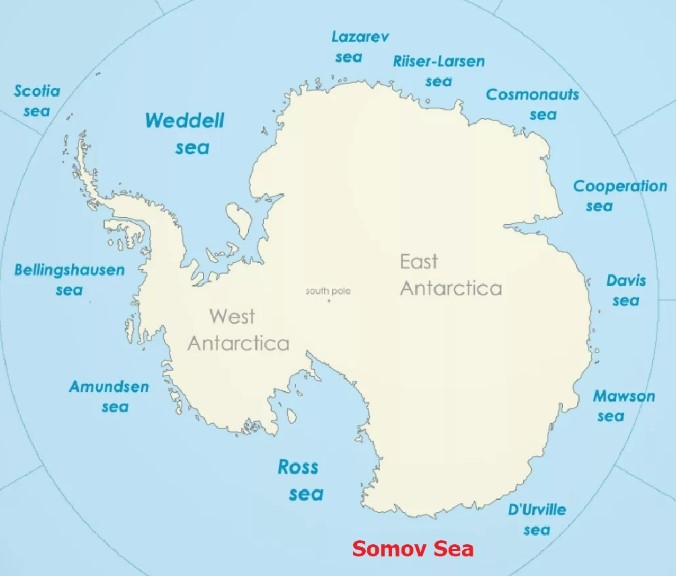 Geographical position of the Somov Sea
Geographical position of the Somov Sea
A marginal sea in the South Pacific Ocean, off the coast of East Antarctica, washing around Victoria Land between 148° and 170° E. It extends west from Cape Adair, where it borders the Ross Sea, to the D'Urville Sea. The coordinates of the central part of the sea are 60°00' S and 162°00' E.
Relief of the Somov Sea
The area of the sea is about 1150 thousand km2, the depth is up to 3000 m. The western part of the sea is mainly on the shelf, the eastern part - partly on the continental slope. In the north there are the Balleny Islands. The coasts are icy, mostly steep, with outlet glaciers. For most of the year the sea is covered with continuous drift ice and icebergs, except in February-March when the ice edge is south of the Balleny Islands.
Climate of the Somov Sea
The sea is dominated by the Antarctic climate, with air temperatures ranging from 0 to -2°C in February and -10 to -20°C in August. The surface water temperature is always close to freezing: from -1.6 to -1.8 °C. The salinity is 34.0-34.3‰.
The waters of the Somov Sea
The sea is almost entirely within the southern polar circle. This means it is covered with ice for most of the year. Only for a few months the ice cover loses its strength and the continental glacier breaks up, sending huge blocks of ice and icebergs into the sea. Several small local cold currents circulate clockwise in the sea area, which also influence the region's climate.
The inhabitants of the Somov Sea
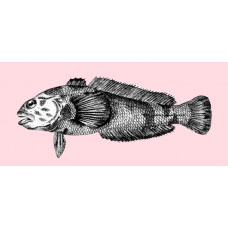
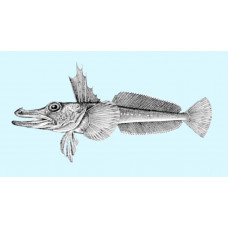
The harsh and cold waters of the Somov Sea are home to many species of unique white-blooded fish that are attracted to large amounts of plankton. There are traditional Antarctic species such as Antarctic toothfish, Patagonian toothfish, Antarctic silverfish, black rockcod, mackerel icefish and unicorn icefish. The Nototheniidae dominate the commercial fishes.
Antarctic silverfish
Latin namePleuragramma antarcticaOther nameAntarctic herringIdentificationThe body of the Antarctic ..
Antarctic toothfish
Latin nameDissostichus mawsoniOther namesAntarctic codIdentificationFirst dorsal fin with 7-9 barb r..
Black rockcod
Latin nameNotothenia coriicepsOther nameAntarctic yellowbelly rockcod, or Antarctic bullhead notothe..
Mackerel icefish
Latin nameChampsocephalus gunnariOther nameChampsocephalus gunnariIdentificationChampsocephalus: Gre..
Nototheniidae
Nototheniidae is a family of fishes of the order Perciformes. 15 genera, more than 50 species (gray,..
Patagonian toothfish
Latin nameDissostichus eleginoidesOther nameChilean sea bass, mero, and icefish.IdentificationThe Pa..
Unicorn icefish
Latin nameChannichthys rhinoceratusOther nameChannichthys rhinoceratusIdentificationChannichthys: Gr..