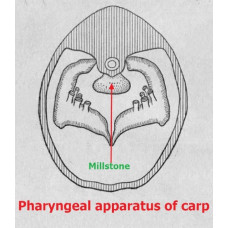
Grindstone - a hard horny formation, appeared instead of the missing upper pharyngeal teeth carp fish, serves as a kind of anvil, where the fish lower pharyngeal teeth crush worms, crush shells of mollusks, chitinous cover of insect larvae, crustaceans.
The cotyledon is surrounded by a muscular "loose body" covering the pharyngeal cavity. Pith and pharyngeal teeth appear at the same time, when the fry loses the nutritious yolk and goes to take food, but in the beginning it is soft and then gradually horny. In some fish, the miller is formed from the fusion of the upper pharyngeal teeth.
In carp fish millstone or chewing plate lies against the pharyngeal teeth and has a different shape: in carp pear-shaped, mustache form isosceles triangle, in the head in youth pentagonal, rounded with the age of fish. It lies on the outgrowth of the occipital bone, horny, but has different hardness in different fish: the carp millstone is hard, and mustache much softer. It depends on the type of food. The size of the millstone is also different: in representatives of the carp family millstones are large according to the size of the pharyngeal teeth rubbing the millstone food, and in bream millstones are small, as the pharyngeal teeth they have thin and the teeth of one bone are in the gaps of the other.
Predators have well-developed teeth both on the jaws and on other parts of the oral cavity (palate, scolex, tongue, etc.). But they serve only to capture and hold the victim. In peaceful fish (herring, carp, etc.) jaw teeth are absent. For grinding food they have adapted pharyngeal teeth and millstone.
Millstone
Tags: millstone